
What to expect after retinal detachment surgeryĪfter the retinal detachment surgery, the eye is patched for 24 hours. If silicone oil was used, a second procedure would be needed to remove it after several weeks to months.
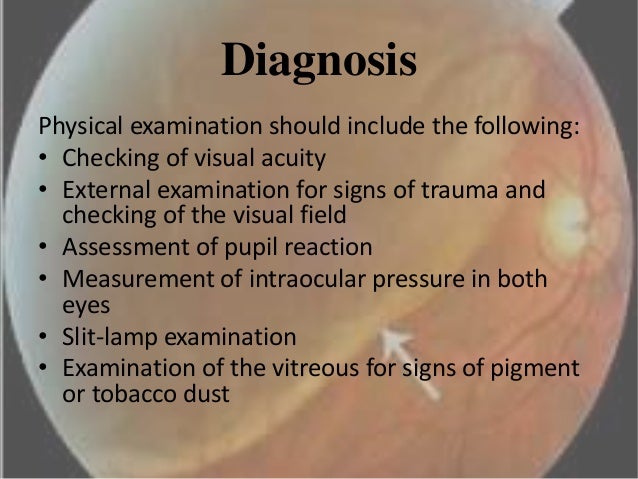
The gas is gradually absorbed by the body over several weeks, and the inside of the eye eventually re-fills with vitreous fluid, which the eye is continually producing. Laser photocoagulation is also used to seal the retinal breaks.
In this procedure, three small incisions are made in the white part of the eye, and tiny instruments are used under microscopic guidance to remove the vitreous (jelly-like fluid) that fills the eye.īecause the eye does not need vitreous to function, the fluid collected under the retina is drained, and a special gas (in some cases silicone oil) is then placed inside the eye to help push the detached retina against the eyewall while it heals. The bubble will reabsorb on its own over a few days. Recovery after this treatment involves special head positioning in order to keep the bubble in the proper place for healing. Once the retina re-attaches, usually within several days, the causative retinal hole is sealed with laser photocoagulation or cryotherapy. This allows the fluid collected behind the retina to be gradually reabsorbed so that the retina can adhere to the eyewall again. This treatment involves a small gas bubble being injected inside the eye in order to plug the retinal tear responsible for the detachment. Pneumatic Retinopexy is an office procedure that may be appropriate in the case of a small detachment caused by a single tear that’s located at the top of the retina. Once the retina is flattened against the eyewall, a laser is used to weld the retinal tears' edges, sealing the leak. The fluid under the detached retina is drained, which allows the retina to settle back into its normal position against the back wall of the eye. This causes the eyewall to indent, counteracting the force pulling the retina out of place. The buckle is placed in a way that doesn't block your vision, and it usually remains in place permanently. Scleral Buckling is a surgical procedure that sews a silicone band (buckle) to the outer white part of your eye (called the sclera) over the area of the retinal tear. The necessary procedure is determined by a retinal specialist based on the specific condition of each individual detachment. There are three surgical options available for repairing detached retinas. Surgery is usually performed within a day or two of the diagnosis of a detachment, particularly if the macula and central vision are not yet affected. Other surgical methods are required to repair it. This is why when the retina has already detached. This is because, with a retinal tear, the eyewall underneath the retina absorbs the energy from the laser to create a scar that fuses the edges of the tear to the eyewall.īecause a detached retina has no contact with the eyewall, there is no surface available to receive the laser energy. While a laser office procedure can be used to treat a retinal tear in order to prevent a retinal detachment, it cannot be used to repair an already detached retina that is no longer in contact with the eyewall. That said, a second operation is sometimes needed. The good news is that 90 percent of retinal detachment surgeries are successful with a single operation. Thinning of the peripheral retina (called lattice degeneration)Īlmost all patients with retinal detachment will need surgery to place the retina back in its proper position.Prior eye surgery, such as cataract removal.A high degree of nearsightedness (myopia).Prior retinal detachment in one eye (gives you a 10% chance of developing a detachment in your other eye).
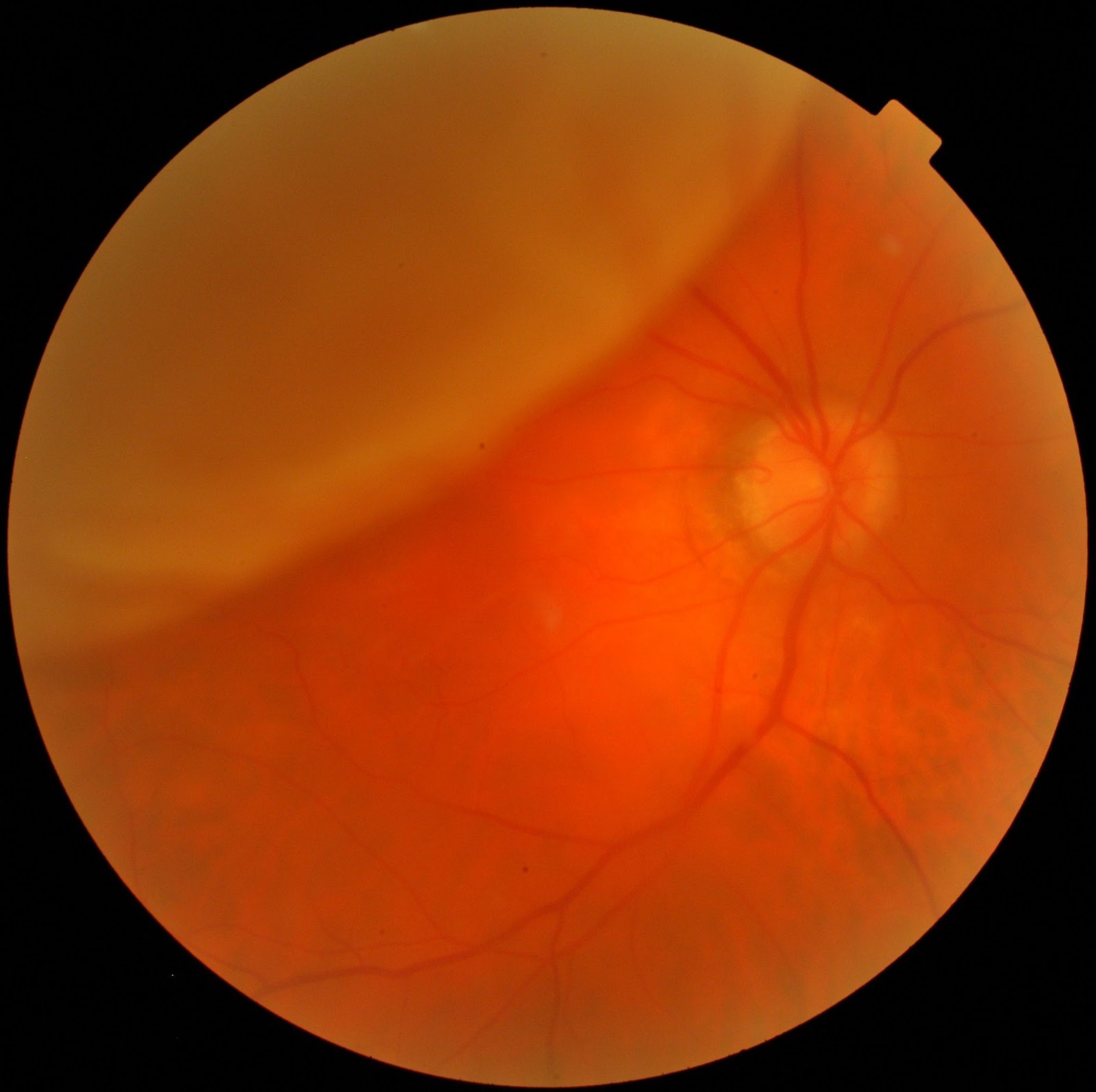
Retinal tear-because vitreous gel tends to pull away from the retina over time, it can tug on the retina and cause a tear that leads to detachment.The following risk factors increase your chance of having a retinal detachment: A sensation of a curtain closing or a fixed shadow which appears in your peripheral field of visionĪ careful eye examination through a dilated pupil is required to diagnose retinal tears or detachment.Flashes of light in the affected eye (a phenomenon known as photopsia).The sudden appearance of many floaters - multiple tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision.If you are experiencing any of the below signs or symptoms of retinal detachment, it is critically important to get immediate medical attention:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
